V2 BlaaS (Blockchain-As-A-Service)
The V2 BlaaS
V2’s BlaaS is a comprehensive infrastructure designed to deploy and manage a variety of blockchain applications. It transcends cloud, portal, and framework boundaries with the aim of revolutionizing the high cost associated with developing and deploying blockchain applications. By providing public resources and interoperability environments akin to the internet, we dramatically cut the costs of development, deployment, operations, maintenance, and regulation of blockchain applications, thereby accelerating the development and universal adoption of blockchain technology.

Current Challenges in the Blockchain Landscape
Development, deployment, and management of blockchain applications are expensive and complex.
Blockchains usually operate independently on different servers or clouds.
Diverse underlying structures and frameworks lead to incompatibility issues.
There’s a shortage of experienced blockchain developers.
Interchain


Capabilities
Purchase BlaaS Resources
Generate Projects And Keys for Connection to Public Chain Nodes
Manage Permissioned Chains
Update Smart Contracts
Handle Off-Chain System Access
Utilize Interchain Services
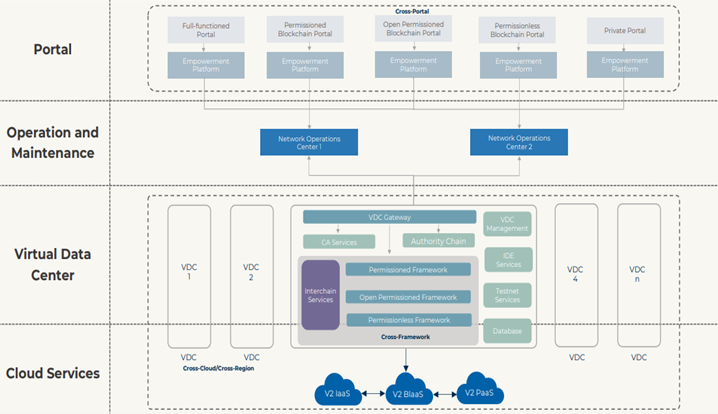
The V2 BlaaS Structure
- Operation & Maintenance
- Cross-chain Training & Development for Developers
- Dapp Contract Development & Deployment
- Developer Framework Training
- Cloud Resource
- An application-agnostic solution that is highly extensible
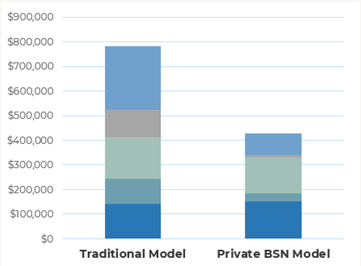
Savings with V2 BlaaS
- An annual cost reduction of 45% overall
- A 66% saving on developer training and operations/maintenance
- An 89% reduction in the development cost of cross-chain services
Example Scenario
- 20 permissioned Dapps on an intranet with one public chain node and one shared permissioned node
- Each Dapp/chain has three peer nodes
- Dapps developed and deployed on Fabric (5), Quorum (7), and Corda (8)
- Dapp configurations: TPS = 10, disk capacity = 500G, identical data usage across both scenarios
BlaaS Use Cases
01
Copyright Protection
02
Procurement
03
E-Government
04
Asset Digitalization
05
Supply Chain Finance
06
Supply Chain Management
07
Internet of Things
08
Contract Management
09
Digital Evidence
10
Agricultural Product Traceability
11
Healthcare
12
Non-Profit
Benefits of V2 BlaaS for Businesses
Key Benefits
Manufacturing
Materials provenance, asset tracking, quality assurance
Energy
Renewable energy certificates tracking, immutable record of mineral rights
Insurance
Simpler and faster claims management, reduced administrative costs
Supply Chain
Improved transparency, traceability, and fraud mitigation
Finance
Verification and transfer of financial information and assets
Healthcare
Unified patient data, drug traceability, and data security
Retail
Better inventory management, faster settlements, and less paperwork
Government
Streamlined and secure public record-keeping and verification functions
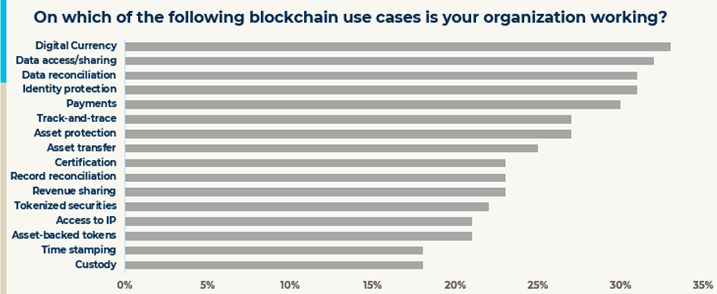
Wide Array of Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Digital Currencies and Payments
Wide Array of Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Digital Currencies and Payments
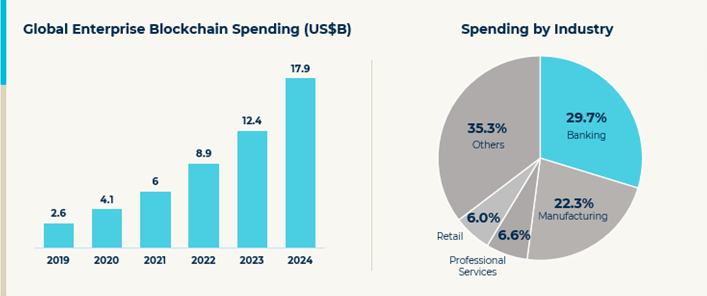
Significant Blockchain Spending Growth in the Enterprise